Lately, we’ve had our eye on SD-WAN. It’s becoming for networks what the Cloud has become for infrastructures and applications. Yet, while the concept of a Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) is generally understood, it is often confused with its technological parent, the Software Defined Network (SDN).
So how can these technologies be so similar and yet so different?
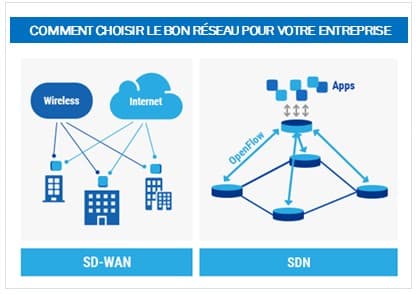
SDN and SD-WAN, almost identical twins :
SDN and SD-WAN are based on the same methodology of separating the control plane from the data plane to make the network smarter. Like identical twins, they may look alike, but they are quite different from each other. The main difference between SDN and SD-WAN lies in their use.
While SDN meets the modern networking needs of managing local area networks (LANs) or operator core networks, SD-WAN is used to connect geographically distributed locations and remote users. Both SDN and SD-WAN can be virtualized to implement additional virtual network functions (VNFs) such as security capabilities and WAN optimization. .
Distinctions between SDN and SD-WAN
SDN is fully programmable by the customer or user, enabling efficient change and configuration management. While SD-WAN is built on SDN technology, programming is managed in the background by the SD-WAN provider, eliminating complexity for the end-user.
SDN focuses on the internal network, whether it’s the LAN or the core service provider network, while SD-WAN concentrates on enabling connections between networks and users over the WAN.
SDN is enabled by NFV (Network Function Virtualization), providing multiple virtualized network functions via software that was previously embedded in closed proprietary systems. In contrast, SD-WAN provides software-defined application routing that can be virtualized and run either virtually or on an SD-WAN appliance.
| Software Defined Network (SDN) | Software Defined WAN (SD-WAN) |
| Manages a local or central service provider network | Enables connections between networks and users across geographical areas |
| User-programmable to provide bandwidth on demand | Programmable to provide operational simplification, integrated safety and traffic prioritization |
| Similar separation of control plane and data plane | Similar separation of control plane and data plane |
| Provides main network performance visibility and real-time analysis | WAN environment visibility and real-time analysis |
| Provides a centralized view for automating network services | Focus on software-defined application routing capabilities |
SD-WAN takes you from the packet world to the application world and beyond
The technology behind SD-WAN shifts the paradigm from packet-based network routing to application-based routing. This enables organizations to use consumer broadband Internet with improved quality and performance, and above all, at a lower cost per megabyte than previously available with MPLS.
SD-WAN also offers agility and flexibility, while maintaining centralized, predefined corporate policies controlling how applications are routed. The resulting visibility and control enable you to identify applications running over the WAN and define policies for their prioritization and use.
SD-WAN also uses dynamic WAN selection to route these applications along the most efficient paths. What’s more, SD-WAN lets you use multiple available links in an “active/active” configuration to provide load balancing and failover, with little to no perceived interruption. Traffic between sites travels over dynamic, fully encrypted tunnels and can be segmented, offering a very high level of security.
Enjoy the best of both worlds
For large companies with an increasingly distributed and complex IT infrastructure, the challenge is to manage the network with total visibility, while having the scalability needed to grow and achieve new business objectives.
With the adoption of cloud-based applications and services, companies are shifting more of their IT capital expenditure (CAPEX) to operating expenditure (OPEX). As they expand, MPLS is simply too expensive to scale their WAN infrastructure, and doesn’t offer the flexibility to deploy remote services.
The combined use of SDN and SD-WAN can support a company’s Cloud-First strategy. Companies can leverage an SDN platform to interconnect global data centers and connect directly to the cloud via a private carrier Ethernet network fabric, and simultaneously reduce WAN complexity by using an SD-WAN overlay to simply extend the perimeter to multiple branch offices and remote users in a secure, orchestrated manner.
Before choosing a network solution for your evolving business, don’t hesitate to talk to the NUMERYX teams. We can help you determine the best solution to your network architecture needs, and provide you with the best thinking on how SDN and SD-WAN will impact your applications and overall security policy.




